How To Use A Finderscope On A Telescope
Finders are essential pointing devices. Now that nosotros have a telescope that will gather light and an eyepiece that will magnify the image, nosotros demand a fashion to accurately indicate the telescope at what we want to see, our target for observation.
Finders take a wider field of view than the typical telescope. Depending on what low ability eyepiece is used, the typical amateur telescope volition likely take a maximum field of view of between .7 degrees and 3 degrees. Naturally, some volition exist narrower and some can be wider, but this is a skillful case range.
This means that yous can only see a minor portion of the sky through the eyepiece. Imagine trying to find something you lost and having to look for it while viewing through the cardboard tube of a roll of toilet paper. Your field of view would be quite modest which would make information technology difficult to discover things.
A finder's field of view can range from about 4 degrees to as wide equally your eye tin see. This makes information technology much easier to notice what you are looking for in the heaven. So the finder and the telescope work together as a team to help you lot locate and see your target.
Also, depending upon our observing location, the blazon of finder y'all may prefer can depend on how dark the sky is, how dark the ground area is and whether we tin come across the target with our unaided centre. If the target is invisible we will crave some optical assist in the finder to see it.
Types Of Finders
Finders autumn into 2 major categories, magnified and unmagnified. Each has its advantage and it is not unusual to take both on larger telescopes.
There are several types of unmagnified finders. These include site tubes, ruddy dot finders and those which present rings projected onto the sky. We will accept a look at each.
Unmagnified finders are typically lower price than the magnified finders, just that does not in any way diminish their value. They just cost less to produce.
Magnified finders are essentially small refractor telescopes. Some are of a directly through design, like half of a binocular. Some have a diagonal that turns the light 45 or 90 degrees to put the finder image in a user-friendly location for the user. Some have a fixed magnification and some can have variable magnification through a zoom feature or replaceable eyepieces. We will discuss them all and provide some examples.
An important part of whatever finder is the mounting subclass. After a finder is mounted on the optical tube, the telescope, you will need to fine melody where information technology is pointing so that it aligns perfectly with the field of view of the telescope. This holder usually has aligning knobs or screws to movement the finder about and so you tin can become the finder and the telescope perfectly aligned. If the holder does non continue the finder firmly in place it will frustrate your efforts to use it.
Finally, for a finder to be useful you take to align it to the scope. Nosotros will become into the alignment of finders later.
Unmagnified Finders
Every bit the name implies, these finders practice not magnify anything. In fact, you usually use these with both eyes open so y'all can see the entire sky every bit yous employ the finder to move the telescope to the target location.
Sight Tube – This consists of a hollow tube with crosshairs at each. You expect through the tube and align the front and back crosshairs on the target to point your telescope. The crosshairs might exist etched on plastic or drinking glass. Sometimes they are a crossed pair of wires at each terminate.
You could hands make a sight tube at home. The longer the tube the more constructive the sight tube will be. Equally long equally you can see the target with your naked eye the sight tube will piece of work.
Sight tubes are typically plant on very low-price telescope packages that you would find in the big box store or perhaps a toy store. They require no batteries and so are maintenance-complimentary. If the subclass is well fabricated and the aligning screws work properly a sight tube can be quite effective.
- Red Dot Finders

Ruby dot finders, RDFs, are the most pop of the unmagnified finders. You will find them on entry-level scopes and on expensive scopes. They project a small red dot onto a plastic or glass plate so that information technology appears to bladder in the sky. You align that dot with the target and your scope is prepare for y'all to view through the eyepiece. Better RDFs take a variable intensity dot and so that you can dim it down so it does not launder out the target.
There are so many examples of red dot finders. Some of the more pop would be:
- The Celestron Star Pointer
- Celestron Star Arrow Pro
- The Orion EZ Finder
- Orion Laser Finder
- Projected Ring Finders

Likely the well-nigh pop of this type of finder is the Telrad. A serial of circles are projected onto a screen so they look like they are floating in the sky. The rings correspond a known field of view and so you can use them to move through the heaven in measured amounts.
As you tin can run into in the picture, the Telrad projects three circles. The smallest ring is ½ degree. Then we accept 2 degree and 4 degree rings.
Telrads can exist used in place of ruby-red dot finders and offer much greater versatility. The rings are extremely useful in star hopping which is a method of finding targets in the sky. If y'all put a starting point star in the center of the band you lot tin can place how far away other stars are that are visible in the Telrad. By moving the rings beyond the star field a known amount you tin can hop from star to star to find a target.
Telrad finder charts accept advantage of these rings. These charts are ordinarily specific to a limited set of targets. The chart shows you where to start and how much to motility the telescopic for each hop as you move the rings across the stars.
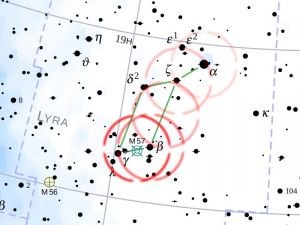
For general use charts, yous can make rings out of wire that cover 4 degrees of your star nautical chart and move them around the star chart to simulate how y'all would movement the Telrad rings around the sky.
The chart shown in the picture has Telrad rings placed on information technology. You would get-go in the upper right which is the bright star Vega. Then you would progress to the side by side star and the adjacent until yous reach the bottom location which would take the Ring Nebula, M57, which is not visible to the naked heart but would be centered in the Telrad central ring.
At present that you have the telescope in the correct location you lot go to your low power eyepiece and look around that area. Sure enough, there it is. This method of finding your targets is called star hopping. The Telrad is one of the best tools available for star hopping.
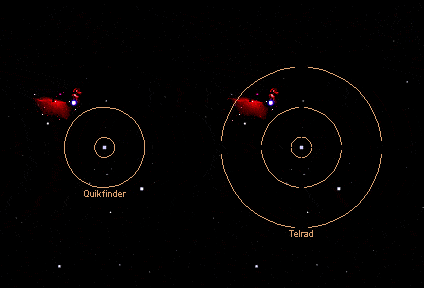
The Rigel Quikfinder is some other example of a projected ring finder. Some people prefer this finder because it is smaller and lighter than the Telrad and volition fit in places the Telrad won't fit.
The Quikfinder projects a ½ degree band and a two caste ring. In the moving picture, y'all tin can run across a comparing of the rings projected past the Rigel quick finder vs. the Telrad.
- Laser Pointer Finder
The laser pointer finder is often based on the same type of hand laser used for presentations. When used at night the laser pointer projects a line into the sky that can exist used to point the telescope. This is not equally precise as a red dot finder or a Telrad, merely it is a quick way to point the scope into the general surface area yous want to view.
Laser finders are all-time used in combination with other finders or telescopes that have a very wide field of view that approaches that of a finderscope. Yous apply the light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation for quick positioning and so go to the other finder or a wide field eyepiece for more precise positioning or star hopping.

In the picture, you see a laser pointer finder mounted on i of my telescopes. I utilise this primarily in the warmer months as the laser does non piece of work very well when information technology is common cold. In the winter I replace it with a red dot finder.
1 affair to take into consideration when using a laser pointer finder is that the projected beam tin can be seen by shipping in the surface area. In fact, if you lot were to bespeak it at an aircraft you could interfere with the pilot'southward vision placing the pilot, the aircraft, and the passengers in danger. Doing so is a criminal act in some areas. Many public observing gatherings ban light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation pointers for this reason.
If you are going to use a laser pointer finder be VERY careful to be certain that there are no aircraft anywhere in the surface area where yous are using the laser. Turn it on merely as long as you require to point the scope, then turn it off.
Another reason that lasers may not be welcome at group observing sessions is that it can interfere with astrophotography. The brilliant laser beam can ruin their exposures. Take these points into consideration before buying a laser pointer finder device.
Magnifying Finders
Magnifying finders are basically modest refractor telescopes. Or yous can recall of them as one-half of a binocular every bit their discontinuity, magnification, field if view, and specifications more closely resemble binoculars.
Mutual specifications for finders are 6X30, 8X50 and 9X50. There are 5X24s available simply they are typically very poor quality often sporting plastic lenses that yield a very poor image. You only come across these on very depression-end telescopes. I would not recommend buying one.
Magnifying finders can have straight through designs, similar a handheld spyglass or binoculars. Or they tin have diagonals, like a telescope, that bends the light to a more than comfortable bending for the user.
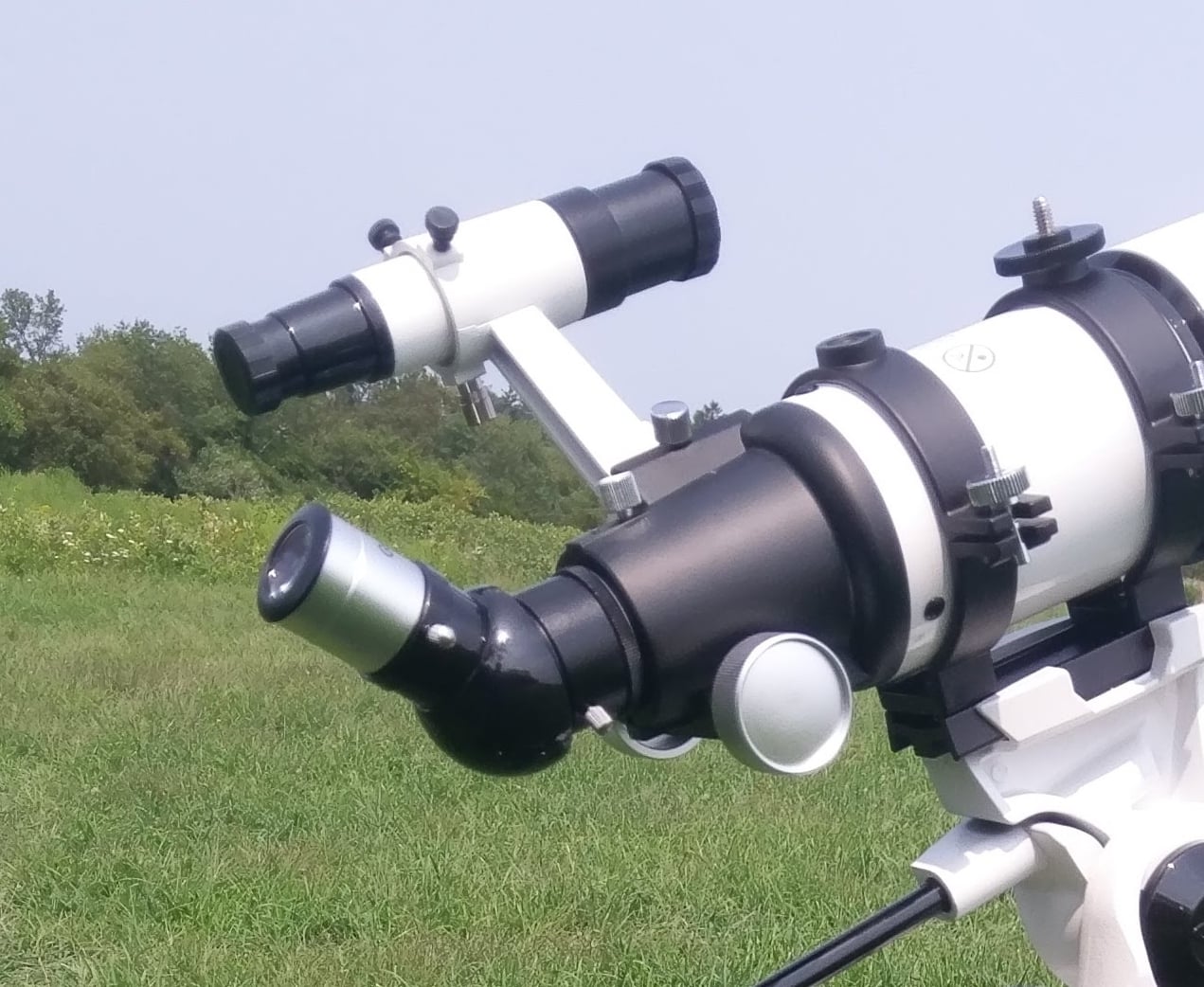

In the picture, we see a 6X30 straight-through finderscope that was included with my 80 mm refractor. The straight through design works well on this telescopic as I use the scope from the rear of the optical tube.
The finder on this telescope is mounted with a standard dovetail shoe. I sometimes bandy this finder out for a carmine dot finder or a laser finder, depending on where I am observing. The magnifying finder works amend for me at more than light polluted areas where I tin see very few stars with my optics. I like the red dot finder better when I have darker sky atmospheric condition and can see more stars with my optics.
The orientation of the image in a magnifying finder tin vary from device to device. Some will present an inverted epitome that is also reversed left to right. Some finders are correct up and down only reversed left and right. This is not as strange as information technology sounds as there is no up and down or left and right in infinite. However, if you are using the finder to star hop information technology tin be a bit confusing at get-go, only most people get used to it.
Then there are the correct paradigm finders. These usually incorporate some kind of prism, similar to a binocular, which corrects the image then that information technology is presented correctly upwardly and down and left to right.
Next, we find the right angle finders. These take a diagonal, similar to the diagonal found on nigh refractor telescopes. This puts the eyepiece of the finder at a 90-degree angle. Depending on what kind of scope you have this may be very desirable.
For case, Newtonian telescopes have the eyepiece on the side. So a right angle finder would place the finder eyepiece in line with the telescope'due south eyepiece. Notwithstanding if y'all are using a refractor or catadioptric, where the eyepiece is at the back of the tube, y'all may find a straight-through finder preferable.
A common designation you should know is the RACI finder. RACI stands for the right angle right image. In the picture, you see the Orion 9X50 RACI finder on my 8" Newtonian telescope. Annotation how conveniently oriented it is compared to the eyepiece. This allows me to move from finder to eyepiece with ease and without having to get upwards from my observing chair.
Too notation that I have a second finder on this telescope, a laser pointer finder. I use the light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation to get into the general area then move to the 9X50 RACI finder to practice my star-hopping or other locating tasks.
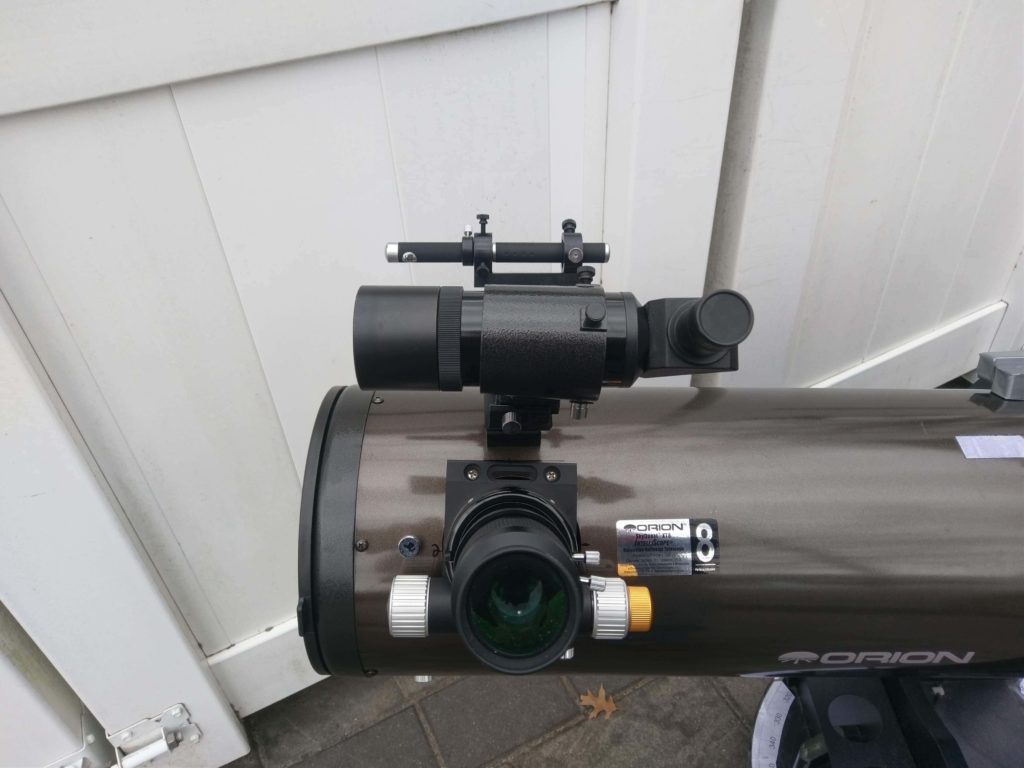

While you lot can add finders directly to your telescope, some would crave you to drill holes to add the mounting shoe. If you would prefer not to do that you tin use a dual finder bracket that fits into the shoe that is already on your scope. This Orion dual finder bracket is a good example. I use i of these on the Newtonian telescopic that is shown in the picture above.
I utilize a laser on this detail scope because a red dot finder would require me to stand or kneel and bend into an awkward position to see the red dot. But the light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation allows me to point the scope without having to bend into hard positions. I practice switch to a red dot finder in the winter, when the light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation does not piece of work well due to the cold. I also switch to the RDF if I am going to be at a large observing session where the light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation might disturb people.
Once finders get past 50 mm in aperture they are often able to have replaceable eyepieces, only similar a regular telescope. In fact, these 60 to eighty mm finders can do double duty when placed on a large telescope that has a long focal length and a narrow field of view.
Having a seventy mm finder with replaceable eyepieces is like having a 2d telescope that is optimized for depression ability broad views. Y'all can use it as your finder or view things just as you would a 70 mm telescope. Its wide field of view will let you lot to see things that the larger scope might not be able to fit into its field of view.
My personal experience is that magnifying finders get more of import and valuable in light-polluted locations. They allow you to see stars that you cannot run across with your eyes solitary. Thus the value of a cherry-red dot finder or Telrad type device may exist reduced since they tin only encounter what you can see with your naked eye. This is a groovy time to team upwards ii types of finders.
Hither are some examples of magnifying finderscopes of different designs.
- Orion 9X50 RACI
- Celestron 9X50 Illuminated Finder
- Astromania 6X30 Finderscope
- Zerone threescore mm Finderscope
- Orion seventy mm Finderscope
Finder Eyepieces
This is a low power eyepiece that maximizes the field of view of your telescope. When used with your other finder(s) this tin can exist a valuable tool when yous are looking for hard to spot targets. Sometimes your target cannot be seen even in your magnifying finder and you have to go to the eyepiece.
My strategy is to always take an eyepiece that gives me the widest possible field of view for each of my telescopes. For refractors with a 1.25" diagonal, this is usually a 32 mm Plossl. For Newtonian, SCT, and MCT telescopes this is unremarkably an eyepiece that will provide the lowest power specified by the manufacturer for your telescope. In this instance, you also desire the credible field of view, AFOV, specification eyepiece.
In a telescope with a 2" diagonal/focuser, this will probable exist an eyepiece of 32 to 40 mm focal length. In order to maximize the field of view, you lot will want an credible field of view in the 65 to 70 degree range.
Naturally, this eyepiece tin can exist used for other purposes than finding. Large targets like the Andromeda Galaxy, the Pleiades, the Hyades, or the Due north America Nebula are very large so you would like to have the widest view eyepiece yous can when viewing them.
So, if y'all read something virtually "finder eyepieces", this is what people are talking about. It is not a special purpose eyepiece, just 1 that maximizes the field of view of your telescope.
Adjustment a Finderscope
Regardless of what kind of finder you are using you lot volition have to align information technology with the telescope. The procedure is adequately simple and is best washed during the twenty-four hours. The key thing is that you are adjustment the finder to the telescope and not the other way around.
Y'all desire to practice this during the day using a fixed land object. At night the things in the sky are moving which makes information technology more difficult to become the alignment correct.
During the mean solar day, set your telescope and then that you can see a distant object, at least ¼ mile abroad and farther is ameliorate. I adopt the cantankerous artillery on a telephone or power pole. That gives me a very well defined target right where the cantankerous arm meets the pole. But the top of a chimney, a letter of the alphabet on a distant sign, or something similar can work as well. This is your alignment target
Here are the steps to follow.
- Using your low ability eyepiece signal the telescope at the target and become it centered in the field of view of the eyepiece. Ignore the finder for now.
- Switch to a high power eyepiece and again, go that target centered
- Lock the telescopic into position in any way you lot can. You don't desire information technology to motility
- Expect through the finder and spot the target
- Using the adjustments on the finder bracket adjust the finder until the target is centered in the finderscope.
- Get back to the eyepiece and make certain the telescopic has not moved. The target should yet be centered
- Check the finder over again and brand whatsoever final adjustments
When the finder and the telescope both are lined upwards on the same indicate on your target, you are all set and ready to take your telescope out nether the stars.
Finders have a tendency to go bumped or moved, specially if you lot accept off at the end of your observing session when you put the telescope abroad. When you first starting time an observing session do a cheque using a bright star. Yous should be able to practice this quickly so the fact that the star is moving should not be a problem.
- Put the star in the center of the finder
- Await through the eyepiece and center the star in the eyepiece
- Go dorsum to the finder and make any small adjustments that may exist needed to heart the star
- Compare the view in the eyepiece and the finder to be sure they concord
This quick melody-up at the commencement of your observing session will save a lot of time throughout the evening as your finder and your telescopic volition be in the best alignment possible for the evening.
Summary
- Finders are an of import role of the telescope package
- They can exist magnifying or unmagnified
- It is not unusual to have more than than one finder on your scope, especially larger telescopes
- Do your initial finder alignment during the day
- Practise a quick finder adjustment at the kickoff of each observing session
I hope yous establish this useful. Don't hesitate to leave a comment below.
Source: https://telescopicwatch.com/how-to-use-align-finderscopes/

0 Response to "How To Use A Finderscope On A Telescope"
Post a Comment